The Coder Design Plan
The Coder Design Plan
The Coder in eurAIka should interact with the user through a Large Language Model (LLM) to solve math and science problems by one of two methods. The first method would be to recognize that a tool exists to directly apply to the problem. In the simplest example, this might be a request to add two numbers together so The Coder should realize that interfacing to a calculator would be appropriate.
The second method of problem solving by The Coder is to generate code in an appropriate computer language, run the code and produce relevant outputs. In either case, The Coder will need to develop a plan to solve the problem, execute the plan and then verify correctness. The LLM should never be used to directly solve the problem.
Rather than attempting to fine-tune an LLM or train it on each language, our proposed solution is to let the LLM learn general coding methodologies and then be able to look up syntax and example code online. The goal is to be able to quickly generate code to solve the user’s particular problem, sacrificing code elegance for speed of solution.
The intent is to use The Coder for small to medium size programming problems. Large scale models like Global Circulation Models (GCMs) or the LIGO gravitational wave detector are best left to experts who have both the software development experience and scientific background.
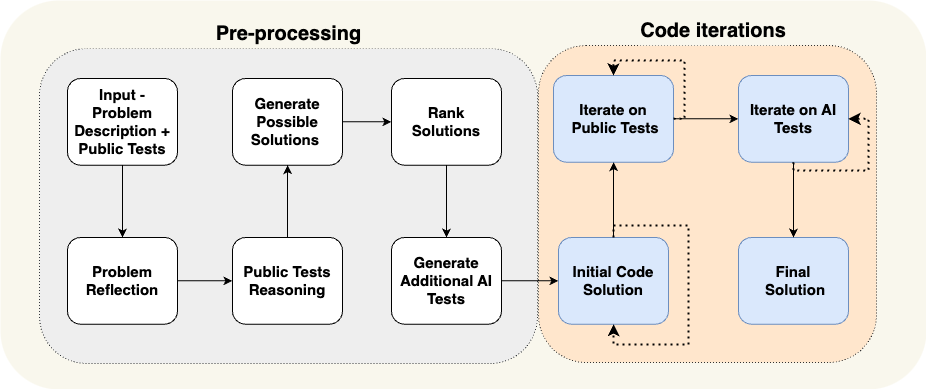
AlphaCodium Flow
A new product from codium.ai released an open-source product, AlphaCodium that has many of the desired characteristics of The Coder. In the Pre-processing stage, AlphaCodium attempts to understand the user’s request through self-reflection and reasoning on public tests, followed by an iterative process of generating code and testing the result.
Problem reflection may be possible as described in the paper by Zhou et al, Self-Discover: Large Language Models Self-Compose Reasoning Structures and enhanced with Large Action Models (LAM) which use an agent-based approach to problem solving.
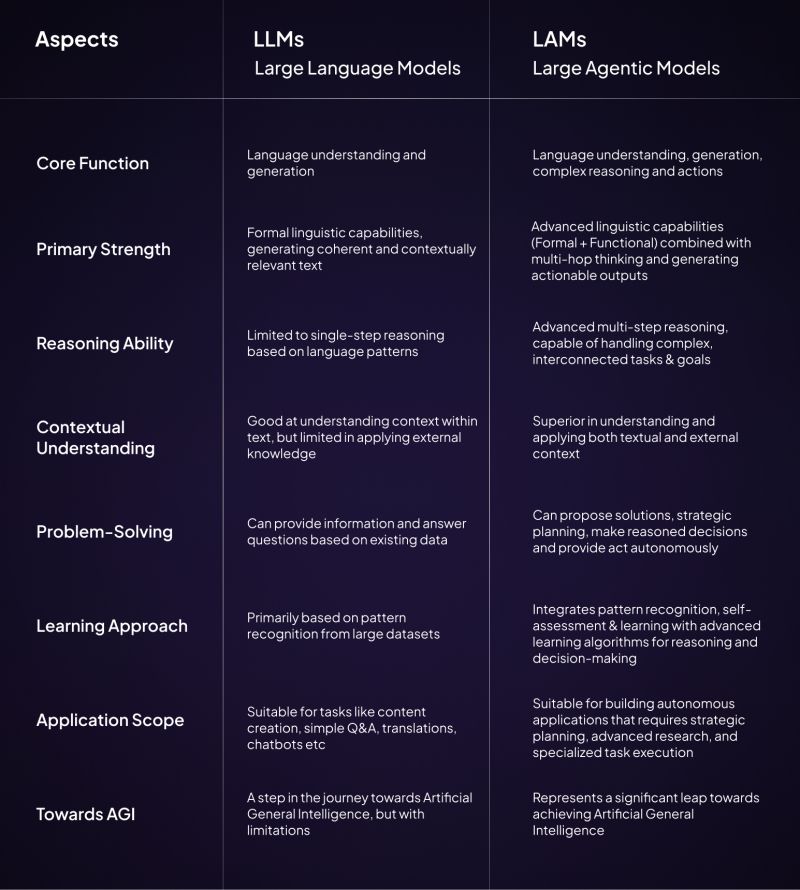
Differences between LLMs and LAMs
Graph-based reasoning might also be a useful technique as available through LangGraph. A project similar to The Coder is Gorilla, “a fine-tuned LLaMA-based model that surpasses the performance of GPT-4 on writing API calls. When combined with a document retriever, Gorilla demonstrates a strong capability to adapt to test-time document changes, enabling flexible API updates and version changes.”
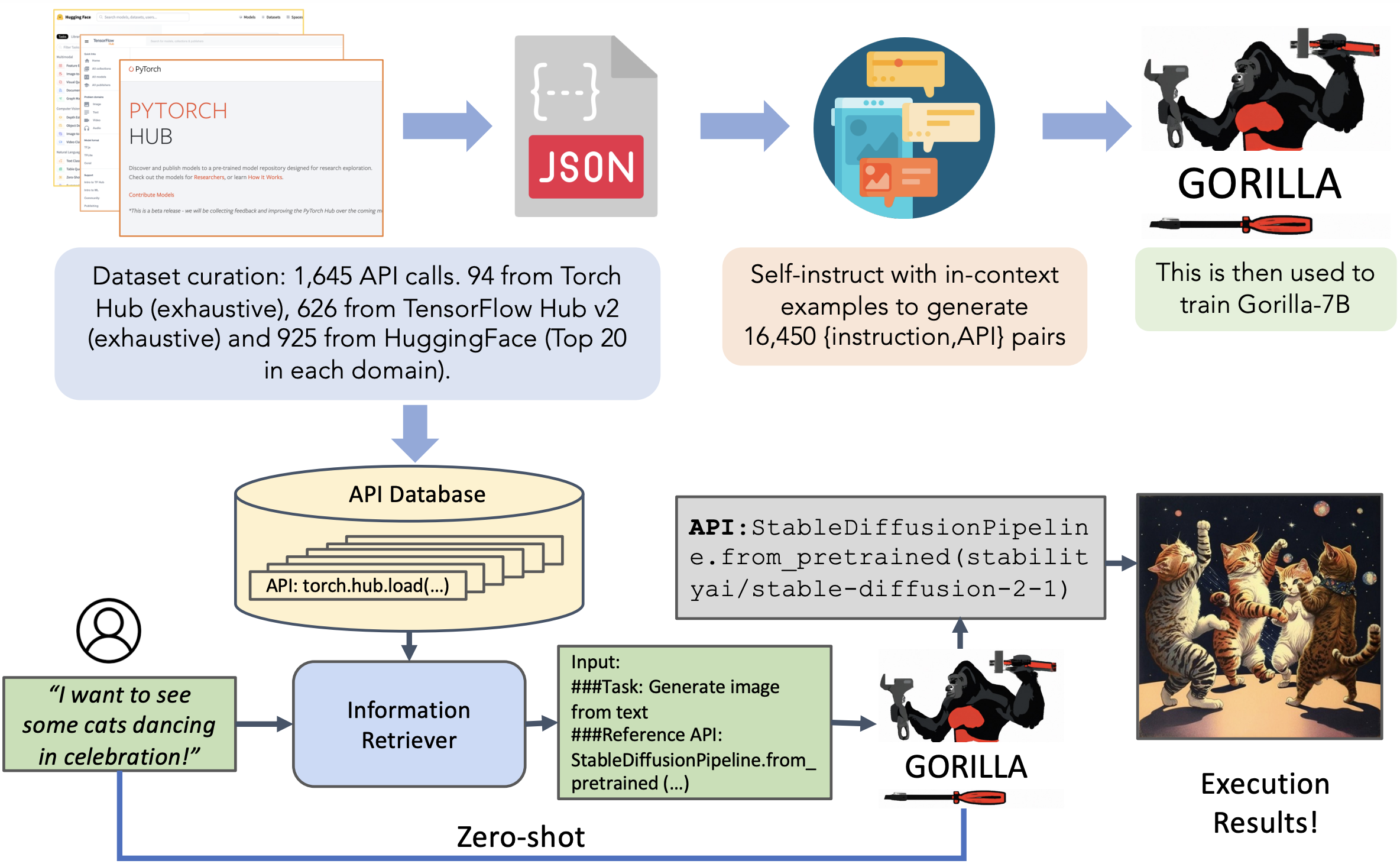
Gorilla flowchart
Instead of dancing cats, can we ask, “Use Mathematica to solve” \(\lim_{n \rightarrow \infty} \left( 8n - \frac{1}{n} \right)^{\frac{-1^n}{n^2}}?\)